India GST guidelines
| FACTSHEET | |
|---|---|
| Country code | IN |
| Tax name | Goods and Services Tax(GST) |
| Tax Authority | Central Board Of Indirect Taxes & Customs |
Overview
Indirect taxes in India is called GST (Goods and Services Tax). It came into effect in July 2017. It replaced several indirect taxes such as VAT, excise duty, services taxes etc. Read more
Registration
The registration in GST is PAN based and State specific. Supplier has to register in each of such State or Union territory from where he effectssupply. A person registered in one State is considered ‘unregistered person’ outside the State.
If a person has unit in SEZ(Special Economic Zone) or is a SEZ developer and also unit in domestic tariff Area (i.e. outside the SEZ) in the same State, then he has to take separate registration for his SEZ unit / as a SEZ developer as a separate place of business of him. The GST law does not have the facility of centralized registration for units across multiple states.
Read more
Who should register for GST
Threshold limits of aggregate turnover for exemption from registration and payment of GST for the suppliers of goods is Rs.40 lakhs and Rs.20 lakhs in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Puducherry, Sikkim, Telangana, Tripura and Uttarakhand with effect from 01.04.2019
Threshold limit of aggregate turnover for exemption from registrationand payment of GST for suppliers of services is Rs.20 lakhs and Rs.10 lakhs in the States of Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura.
Where to register?
Visit GST portal. Go to Services > Registration > New Regisrtration.
Tax Registration number - GSTIN
Once GST regsitration is complete a supplier is issued a 15 digit GST identification number(GSTIN). The first 2 digits of the GSTIN is the State code, next 10 digits are the PAN of the legal entity, the next two digits are for entity code, and the last digit is check sum number. Registration under GST is not tax specific which means that there is a single registration for all the taxes i.e. CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST and cesses
GSTIN Format
Regular Registration
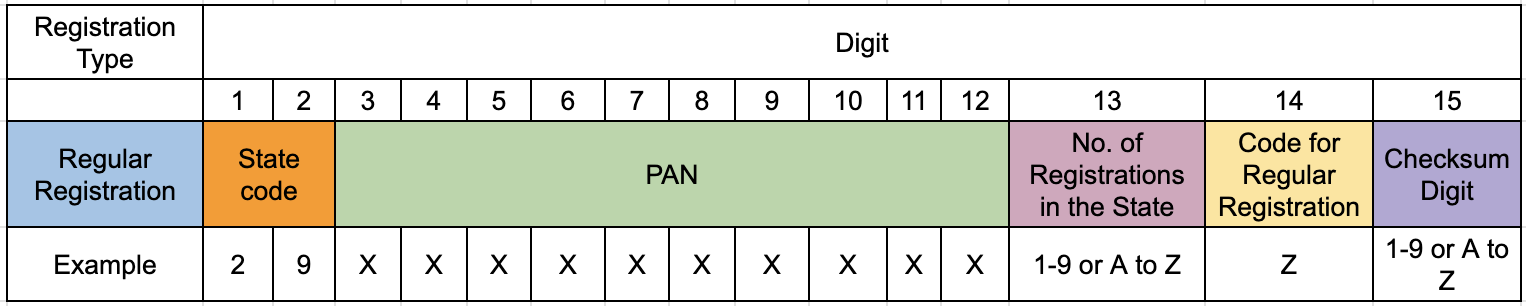
Following are the details of the GSTIN format
- 1st 2 digits: This is the state code as per the Indian Census 2011
- Next 10 digits:This is the PAN of the business entity.
- 13th digit: This denotes the serial number of registrations the business entity has for business verticals in the state, under the same PAN. It can range from 1-9 for businesses with up to 9 business vertical registrations in the state and for more than 9 registrations, from A-Z.
- 14th digit:This will be ‘Z’ by default.
- 15th digit: This digit denotes a ‘checksum’. It may be an alphabet or a number.
Regular Expression(Regex)
\d{2}[A-Z]{5}\d{4}[A-Z]{1}[A-Z\d]{1}[Z]{1}[A-Z\d]{1}
Non Resident Taxable Persons (NRTP) for OIDAR Sevices (Online Information Data Base Access and Retrieval)
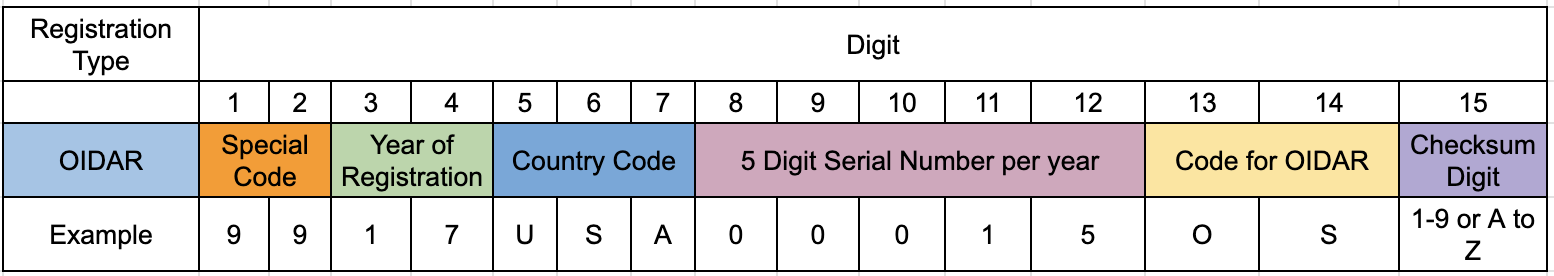
- Special Code 99 for 'Other Country'
- Special Code 97 for 'Other Terrritory'
Tax rates
On Intra state transactions CGST and SGST/UTGST are applied. In case of intersate transction IGST is appiled . Following are the currently allowed tax rates. Along with these 'cess' might be levied by the state governments on some items
| CGST (%) | SGST (%) | IGST (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 |
| 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 |
| 1.5 | 1.5 | 3 |
| 2.5 | 2.5 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 | 12 |
| 9 | 9 | 18 |
| 14 | 14 | 28 |
| 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
Invoice Format
There is no particular prescribed format but the following fields are mandatory
- Name, address and GSTIN of the supplier
- A consecutive serial number, in one or multiple series, containing alphabets or numerals or special characters like hyphen or dash and slash symbolised as “-” and “/” respectively, and any combination there of, unique for a financial year
- Date of its issue
- Name, address and GSTIN or UIN, if registered, of the recipient
- Name and address of the recipient and the address of delivery, along with the name of State and its code, if such recipient is un-registered and where the value of taxable supply is fifty thousand rupees or more
- HSN code of goods or Accounting Code of Services
- Description of goods or services
- Quantity in case of goods and unit or Unique Quantity Code there of
- Total value of supply of goods or services or both
- Taxable value of supply of goods or services or both, taking into account the discount or abatement, if any
- Rate of tax (Central tax, State tax, Integrated tax, union territory tax or cess)
- Amount of tax charged in respect of taxable goods or services (Central tax, State tax, Integrated tax, union territory tax or cess)
- Place of supply along with the name of State, in case of a supply in the course of inter-State trade or commerce
- Address of delivery where the same is different from the place of supply
- Whether the tax is payable on reverse charge basis
- Signature or digital signature of the supplier or his authorized representative
Einvoicing in India
Einvoicing is mandatory for businesses with a turnover of more than Rs.20 crores. This is the revised threshold limit as per the notification on Feb'22 with effect from 1st day of April, 2022.
Einvoicing in india is enabled by Invoice Regsritaion Portal (IRP). Invoices issues by the supplier has to be regestered with the IRP. On successful registration IRP returns a QR code and an IRN(invoice reference number). The QR code has to be affixed on the invoice before sending it to the buyer. Some supplier also add the IRN number on the invoice in addition to the QR code.
Note that IRP portal is registration network and not an einvoice delivery network. This implies that merchants have to send the invoice to the receivers themselves after registering it with the IRP. This is in contrast with other einvoicing networks such as Peppol, which sends the einvoices to the end receipient.
Auto-population of einvoice for returns filing
The invoices successfully registered on the IRP will be automatically popluated on GSTR-1. This will be available for download as an excel file. Read more..
State code
It is noticed that the state codes defined by the GST council doesnot match with the ISO code.
Exemptions
Offenses
Following are considered as offenses under GST law.
- Making a supply without invoice or with false/incorrect invoice;
- Issuing an invoice without making supply;
- Not paying tax collected for a period exceeding three months;
- Not paying tax collected in contravention of the CGST/SGST Act for a period exceeding 3 months;
- Non deduction or lower deduction of tax deducted at source or not depositing tax deducted at source under section 51;
- Non collection or lower collection of or non- payment of tax collectible at source under section 52;
- Availing/utilizing input tax credit without actual receipt of goods and/or services;
- Fraudulently obtaining any refund;
- Availing/distributing input tax credit by an Input Service Distributor in violation of Section 20;
- Furnishing false information or falsification of financial records or furnishing of fake accounts/documents with intent to evade payment of tax;
- Failure to register despite being liable to pay tax;
- Furnishing false information regarding registration particulars either at the time of applying for registration or subsequently;
- Obstructing or preventing any official in discharge of his duty;
- Transporting goods without prescribed documents;
- Suppressing turnover leading to tax evasion;
- Failure to maintain accounts/documents in the manner specified in the Act or failure to retain accounts/documents for the period specified in the Act;
- Failure to furnish information/documents required by an officer in terms of the Act/Rules or furnishing false information/documents during the course of any proceeding;
- Supplying/transporting/storing any goods liable to confiscation;
- Issuing invoice or document using GSTIN of another person;
- Tampering/destroying any material evidence;
- Disposing of/tampering with goods detained/seized/attached under the Act.
Penalty
Any taxable person who has committed any of the offences shall be punished with a penalty that shall be higher of the following amounts:
- The amount of tax evaded, fraudulently obtained as refund, availed as credit, or not deducted or collected or short deducted or short collected, or
- A sum of Rs.10,000/-
Any registered person who has not paid tax or makes a short payment of tax on supplies shall be a liable to penalty which will be the higher of:
- 10% of the tax not paid or short paid, or
- A sum of Rs.10,000/-
Any person who contravenes any provision of the Act or the rules made under this Act for which no separate penalty has been prescribed shall be punishable with a penalty that may extend to Rs.25,000/-
Frequently Asked Questions
Details
Details
Details
Details
Important Wesbites
| Description | Website |
|---|---|
| GST council | Website |
| GST law | Website |
| GST State code | Official Pdf |
| HSN code search | Website |
| GST rates | Wesbite |
| Help Desk Number | 1800-103-4786 |
| GSTIN Lookup | Search |
| GST Login | Visit Website |
| Notifications | GST Notifications |
Latest updates
10-May-2023E-Invoicing threshhold limit reduced to Rs. 5 Crore from 01st August 2023- CBIC issued a notification mandating businesses with turnover of over 5 crore required to generate e-invoice from August 1. The current limit is 10cr. Learn More
06-May-2023Deferment of implementation of time limit on reporting old einvoices- The imposition of time limit of 7 days on reporting old e-invoices on the e-invoice IRP portals for taxpayers with aggregate turnover greater than or equal to 100 crores has been deferred by three months Learn More
13-Apr-2023Time limit for reporting invoices on the IRP portal- The invoices should be reported to IRP within 7 days of generation. This is applicable to businesses with annual turnover of 100Cr and above. Learn More
- Example, if an invoice has a date of April 1, 2023, it cannot be reported after April 8, 2023
