United Kingdom VAT guidelines
| FACTSHEET | |
|---|---|
| Country code | UK |
| Tax name | VAT |
| Tax Authority | HM Revenue & Customs |
Overview
United Kingdom follows Value Added Tax (VAT) scheme as the consumption tax. VAT is applied to the value added at each stage of the production and distribution chain. It's ultimately paid by the end consumer.
Tax Rates
-
Standard Rate: 20%
- Applicable to the majority of taxable supplies, with specific exemptions.
-
Reduced Rate: 5%
- Applies to certain goods and services, such as children's car seats and household energy.
-
Zero Rate: 0%
- Covering items like books, newspapers, periodicals (including digital versions), and specific types of food products.
-
Flat Rate Scheme
- Under this scheme, you remit a predetermined VAT rate to HMRC. You retain the surplus between your customer charges and the VAT payment to HMRC. With the exception of specific capital assets valued at over £2,000, you are not permitted to recover VAT on your purchases. To be eligible for participation in this scheme, your VAT turnover must not exceed £150,000 (exclusive of VAT), and you are required to make an application to HMRC.
Registration Threshold
£85,000 - Businesses based in Uk are requried to register for VAT if the total VAT taxable turnover for the last 12 months was over £85,000.
Who should register ?
Registration to HMRC is required under following circumstances
- The cumulative VAT taxable turnover within the preceding 12-month period exceeded £85,000 (the VAT threshold).
- Forecasts indicate that your turnover will surpass £85,000 in the upcoming 30 days.
- Non-established taxable persons (NETPs) are subject to these conditions regardless of the VAT threshold.
- While being situated in Northern Ireland and dealing in VAT-exempt goods or services, you procure goods valued at over £85,000 from EU VAT-registered suppliers for business purposes.
How to enroll for VAT in the UK?
VAT registration can be done in two ways
- Online registration by utilizing the Government Gateway user ID and password.
- Opt for registration through an agent.
Time of supply a.k.a tax point
This is the specific date that is considered for tax purposes when a transaction occurs.
There are different scenarios where the corresponding Tax Points can vary. Following are some examples
- When no invoice is required → The date of supply
- When a VAT invoice is issued → The date of the invoice
- When a VAT invoice is issued 15 days or more after the date of supply → The date when the supply actually occurred
- When payment or an invoice is issued in advance of the supply → The earlier of the date of payment or the date of the invoice
The date of supply is defined as follows:
- For goods: It is the date when they are dispatched, collected, or made available, such as when they are installed in the customer's residence.
- For services: It is the date when the service work is completed.
Non residents (NETPs)
Who is a NEPT ?
A Non-Established Taxable Person (NETP) refers to an individual or entity that lacks regular residence in the UK, does not maintain a physical presence or establishment in the UK, and, in the case of a company, is not legally incorporated in the UK.
If you qualify as an NETP and engage in any taxable transactions in the UK, irrespective of their monetary value, including the provision of digital services, you are obligated to register for VAT.
Regsitration for NETPs
Registration is required if you’re an NETP and you make any taxable supplies in the UK, regardless of their value and including supplies of digital services
VAT number format
The tax identification number in UK is called VAT number. The format is as follows. VAT number has either 9 or 12 numbers, sometimes with ‘GB’ at the start, like 123456789 or GB123456789. You can check the validity of UK VAT number from the official HMRC site or a Vat validation provider like Lookuptax.
Invoice format
| Full Invoice | Simplified Invoice | Modified Invoice | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unique invoice number that follows on from the last invoice | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Your business name and address | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Your VAT number | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Date | Yes | No | Yes |
| The tax point (or 'time of supply') if this is different from the invoice date | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Customer's name or trading name, and address | Yes | No | Yes |
| Description of the goods or services | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Total amount excluding VAT | Yes | No | Yes |
| Total amount of VAT | Yes | No | Yes |
| Price per item, excluding VAT | Yes | No | Yes |
| Quantity of each type of item | Yes | No | Yes |
| Rate of any discount per item | Yes | No | Yes |
| Rate of VAT charged per item - if an item is exempt or zero-rated, make clear no VAT on these items | Yes | Yes (1) | Yes |
| Total amount including VAT | No | Yes (1) | Yes |
(1) - In the case of a Simplified or Modified invoice, the total amount including VAT is required.
Credit Note Format
The credit or debit note you generate must include the following
- same information as the VAT invoice
- reason why it was issued
- total amount credited, excluding VAT
- number and date of the original VAT invoice
Domestic Reverse Charge
The reverse charge mechanism is applicable exclusively to supplies that meet the following criteria:
- The supplies must be specified supplies of goods or services.
- The recipient (your customer) is either registered for UK VAT or is obligated to register.
- Your customer acquires the goods or services for business purposes.
- In the case of specified goods, such as mobile phones or computer chips, the VAT-exclusive value exceeds the de minimis limit.
Specified goods encompass mobile phones, computer chips, wholesale gas, and wholesale electricity. Specified services comprise emission allowances, wholesale telecommunications, renewable energy certificates, and construction services.
Supplies subject to the reverse charge are not eligible for the Flat Rate Scheme.
Businesses that employ the cash accounting scheme must exclude sales and purchases subject to the reverse charge from the scheme. These supplies should be reported under the reverse charge regulations when submitting returns.
For a detailed understanding of the Domestic Reverse Charge procedure, you can refer to VAT Notice 735.
Invoice Notes for Reverse Charges
When your customer is responsible for remitting the VAT, the invoice must bear the specific reference 'reverse charge.' Several examples comply with this legal requirement, including:
- "reverse charge: VAT Act 1994 Section 55A applies"
- "reverse charge: S55A VATA 94 applies"
- "reverse charge: Customer to pay the VAT to HMRC"
The invoice should clearly indicate the amount of VAT subject to the reverse charge, but this amount should not be included in the total VAT charged.
If your billing system cannot display the reverse charge amount, the wording should convey that VAT is to be accounted for by your customer at the standard VAT rate, based on the VAT-exclusive selling price for the reverse charge goods or services.
Sample invoice with reverse charge
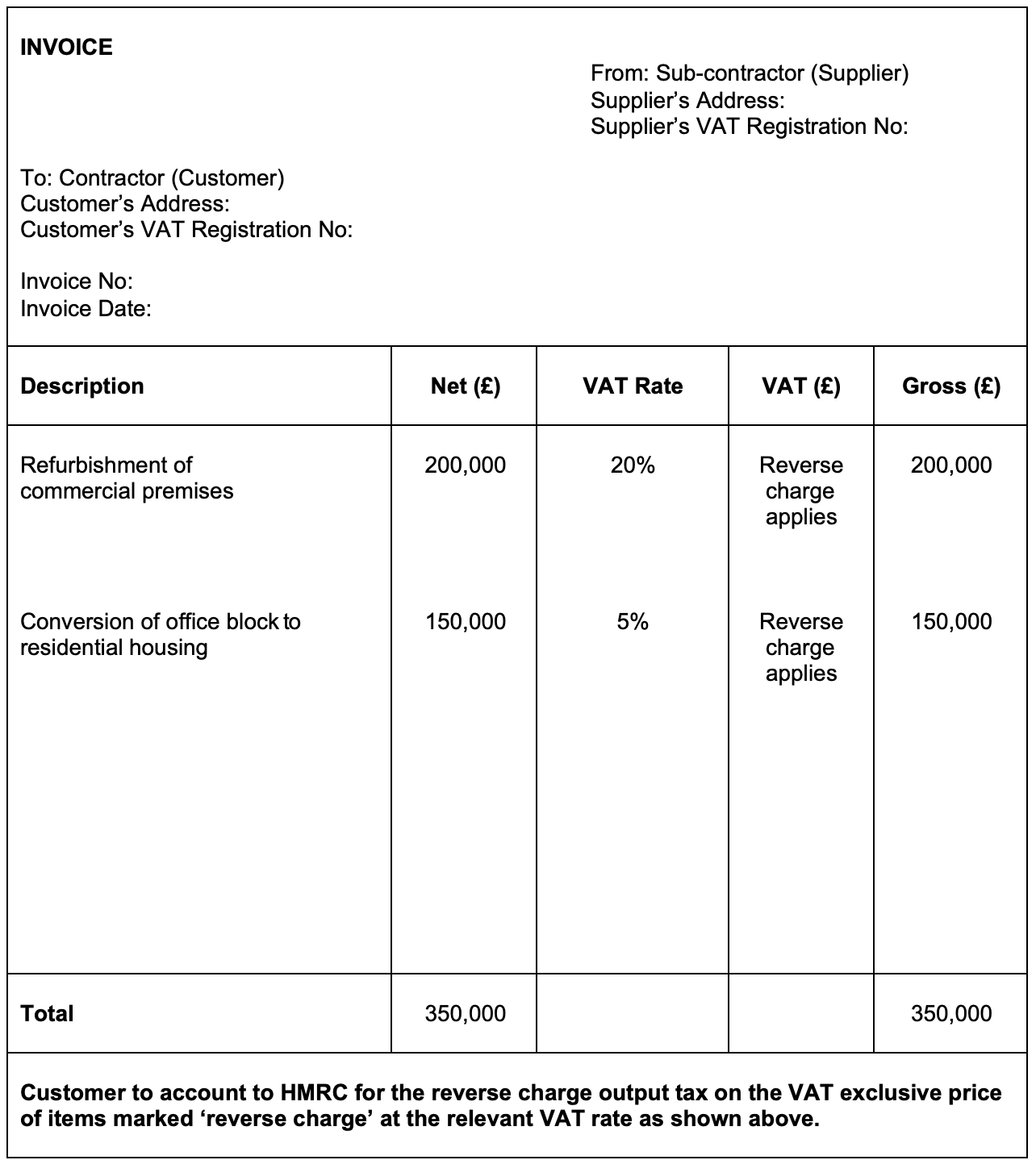
For reference, you can view a sample invoice that illustrates the application of the reverse charge mechanism at the following link: Sample Invoice.
Credit Notes for Reverse Charges
Suggested phrasing for credit notes related to reverse charges includes:
- "reverse charge: customer to account for the output tax adjustment of – £[enter the amount] to HMRC"
- "reverse charge: UK customer to account for the output tax adjustment of – £[enter the amount] to HMRC"
- "customer to account to HMRC for the adjustment to reverse charge output tax on the VAT-exclusive price of items marked reverse charge"
Cross-Border Reverse Charges
The reverse charge mechanism is employed in cases where:
- The place of supply is the United Kingdom.
- The supplier is situated outside the United Kingdom.
- You, as the recipient, are located within the United Kingdom.
- The supply is not exempt, which includes supplies that are subject to an option to tax.
- For supplies falling outside the general rule, you are registered for VAT in the United Kingdom.
The reverse charge applies to nearly all business-to-business (B2B) service supplies, except for those that are exempt, unless specific 'use and enjoyment' provisions are in effect.
This mechanism comes into play when you, as the customer, receive services. In such cases, you are required to assume the roles of both the supplier and the recipient of the services. It is applicable even if your supplier, despite having a UK VAT registration number, is based outside the United Kingdom.
For instance, if you receive telecommunication services from a supplier in the USA and utilize those services within the USA, although they would typically be taxable in the UK under the B2B general rule, specific use and enjoyment rules are applicable.
Digital Products
If your business provides digital services to consumers in the UK, these services are subject to UK VAT. However, if you offer digital services to consumers outside the UK, they are exempt from UK VAT.
When you distribute digital services to consumers through a third-party platform or marketplace, it is the responsibility of the digital platform to account for VAT on the supply, relieving your business of this obligation.
Selling Digital Products to the EU
If you're a UK-based business offering digital services to consumers in the EU, the place of supply is determined by the consumer's location.
You have two options:
- Register for the Non-Union VAT MOSS scheme in an EU member state.
- Register for VAT in every EU member state where you provide digital services to consumers.
Validating if the customer is a business
Apart from validating VAT number using services like Lookuptax, merchants can also accept alternative evidence such as website detail that the customer is in business incase they cant provide the vat number. Its the merchant's discretion and customer cannot ask you to treat a supply as business-to-business if they have not given a valid VAT registration number
Location determination
Merchants are expected to gather evidence of the location of the customer while seliing digital goods and services. Here are the requisite pieces of evidence that the seller must gather for digital services:
- The residential billing address of the consumer.
- The Internet Protocol (IP) address of the device utilized by the consumer.
- The consumer's banking information.
- The country code of the SIM card used by the consumer.
- The location of the consumer's fixed landline through which the service is provided.
- Any other commercially pertinent information, such as product coding data that electronically links the transaction to a specific jurisdiction.
For businesses engaged in cross-border digital service provision, it is necessary to obtain and maintain two pieces of information as proof of the consumer's habitual residence.
- During the point of sale, request the consumer to provide either of the following:
- billing address, including the country
- telephone number, including the country dialling code
- When the consumer makes a payment for the digital service, it is essential to obtain a notification from the payment service provider, which contains the two-digit country code of the consumer's residential country, as recorded in their information.
If these two pieces of information match, it will suffice to establish the consumer's location, and you can document these details in your accounting records.
Digital portals, platforms, gateways and marketplaces
If the platform operator recognizes you as the seller, establishes the general terms and conditions, authorizes payments, or manages the delivery or download of the digital service, then it becomes the platform operator's responsibility to account for the VAT payment imposed on the consumer.
Foreign currency invoice
This is applicable only if you are selling to your customers in UK in a foreign currency other than sterling. For VAT-related purposes, it is imperative to convert all purchases or sales into British Pounds (sterling). This conversion should be performed when you document the transaction in your VAT records to represent the transaction in sterling.
If the transaction is subject to UK VAT, your invoices must additionally display the following details in sterling:
- The total net value of goods and services at each VAT rate.
- The applicable VAT amount, if any, at each rate.
There is no requirement to display sterling figures for each line item on the invoice.
Exchange rates
You can use the following methods to get the FX rates for printing on your foreign currency invoices
- UK market selling rate at the time of the supply. The rates published in national newspapers are acceptable.
- Exchange rates published by HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). This is known as the ‘period rate of exchange’
VAT returns
A VAT Return is a document that you complete to inform HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) about the amount of VAT you've invoiced to your customers and the amount you've paid to other businesses.
VAT Returns filling frequency
Typically, you are required to send a VAT Return to HMRC every quarter, which is referred to as your 'accounting period.'
If you are VAT-registered, it's mandatory to submit a VAT Return even if you don't owe any VAT or have any VAT to reclaim.
Another method for reporting VAT is referred to as "payments on accounts," which involves making an advance payment of VAT. The deadline for this is usually one calendar month and seven days after the conclusion of your accounting period, and this deadline also coincides with the date for settling your VAT liability to HMRC. It's important to factor in the time needed for your payment to be received by HMRC.
VAT Return format
You should ensure that your VAT Return contains the following details:
- The total sum of your sales and purchases.
- The amount of VAT that you are liable to pay.
- The amount of VAT that you are eligible to reclaim.
- The amount of VAT owed to you by HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC), provided you are seeking reimbursement for VAT associated with business expenses.
It's essential to account for the VAT based on the entire value of your sales, even in situations where:
- You receive goods or services as payment, such as in a part-exchange scenario.
- You have not levied any VAT on the customer; in such cases, the total price you charge is considered to include VAT.
If you are VAT-registered in Northern Ireland, it is necessary to incorporate EU sales in your VAT Return and also complete an EC Sales List.
Sending an inaccurate return can result in a penalty of up to 100% of any erroneously stated or over-claimed tax.
To manage import VAT on your VAT Return, you can utilize 'postponed VAT accounting.' This system enables you to report import VAT and subsequently reclaim it as a business expense within the same VAT Return.
VAT payments
Both online and offline payment methods are available for payments The VAT you pay is usually the difference between any VAT you’ve paid to other businesses, and the VAT you’ve charged your customers.
Record Keeping
Retention of VAT Records:
You are required to retain VAT records for a minimum of 6 years. This duration extends to 10 years if you are utilizing the VAT One Stop Shop (OSS) scheme or have previously used the VAT Mini One Stop Shop (MOSS) scheme.
Digital Record-Keeping:
Your digital records should encompass the following:
- VAT associated with the goods and services you provide (supplies made).
- VAT linked to the goods and services you receive (supplies received).
- Details regarding the 'time of supply' and the 'value of supply' (value excluding VAT) for all your purchases and sales.
- Any adjustments you make to a return.
- Records related to reverse charge transactions, where you document VAT for both the sale price and the purchase price of goods and services you acquire.
- Information pertaining to any VAT accounting schemes you participate in.
- If you operate under a retail scheme, your overall daily gross takings.
- If you use the Flat Rate Scheme, the items for which you can claim VAT.
- For those involved in gold trading and utilizing the Gold Accounting Scheme, your total sales and the associated VAT.
Digital Linking of Records:
If you use multiple software packages or products for record-keeping and return submission, you must establish digital links between them. Manual data transfer or 'copy and paste' methods are not permitted. Digital linking can be achieved through various means, such as:
- Employing formulas to link cells in spreadsheets.
- Transmitting records via email.
- Storing records on a portable device to provide to your agent.
- Importing and exporting XML and CSV files.
- Downloading and uploading files as required.
